Displaying news 31 - 60 of 516 in total
Five days before NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope ended its mission on Jan. 30, 2020, scientists used the spacecraft's infrared camera to take multiple images of a region known as the California Nebula — a fitting target considering the mission's management and science operations were both based in Southern California at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Caltech.
For the first time, scientists have directly measured wind speed on a brown dwarf, an object larger than Jupiter (the largest planet in our solar system) but not quite massive enough to become a star. To achieve the finding, they used a new method that could also be applied to learn about the atmospheres of gas-dominated planets outside our solar system.
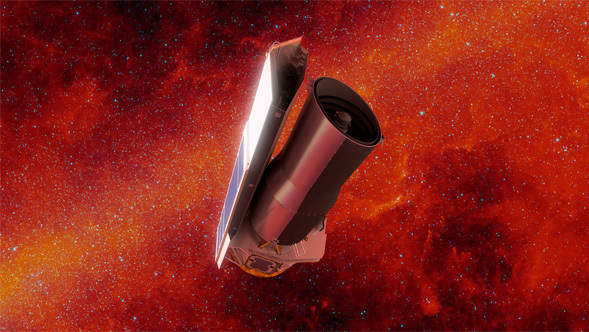
After more than 16 years studying the universe in infrared light, revealing new wonders in our solar system, our galaxy and beyond, NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope's mission has come to an end.
The Tarantula Nebula, seen in this image by the Spitzer Space Telescope, was one of the first targets studied by the infrared observatory after its launch in 2003, and the telescope has revisited it many times since. Now that Spitzer is set to be retired on Jan. 30, 2020, scientists have generated a new view of the nebula from Spitzer data.
In the scorching atmosphere of exoplanet KELT-9b, even molecules are torn to shreds.
A new virtual reality experience lets users get a taste of what it's like to explore the cosmos with the Spitzer Space Telescope, one of NASA's four Great Observatories.
NASA is celebrating the legacy of one of its Great Observatories, the Spitzer Space Telescope, which has studied the universe in infrared light for more than 16 years. The Spitzer mission will come to a close on Jan. 30.
NASA will host a live program at 1 p.m. EST Wednesday, Jan. 22, to celebrate the far-reaching legacy of the agency’s Spitzer Space Telescope – a mission that, after 16 years of amazing discoveries, soon will come to an end.
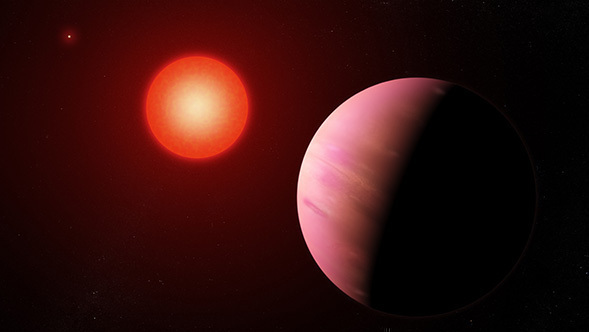
NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite has discovered its first Earth-size planet in its star's habitable zone, the range of distances where conditions may be just right to allow the presence of liquid water on the surface. Scientists confirmed the find, called TOI 700 d, using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and have modeled the planet's potential environments to help inform future observations.
This image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows the Perseus Molecular Cloud, a massive collection of gas and dust that stretches over 500 light-years across. Home to an abundance of young stars, it has drawn the attention of astronomers for decades. Spitzer's Multiband Imaging Photometer instrument took this image during Spitzer's "cold mission," which ran from the spacecraft's launch in 2003 until 2009, when the space telescope exhausted its supply of liquid helium coolant.
Look closer to see why scientists studying this distant cloud of dust and gas think it resembles a cosmic jack-o'-lantern.
This infrared image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows a cloud of gas and dust full of bubbles, which are inflated by wind and radiation from young, massive stars. Each bubble is filled with hundreds to thousands of stars, which form from dense clouds of gas and dust.
NASA launched its Spitzer Space Telescope into orbit around the Sun on Aug. 25, 2003. Since then, the observatory has been lifting the veil on the wonders of the cosmos, from our own solar system to faraway galaxies, using infrared light.
A new study using data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope provides a rare glimpse of conditions on the surface of a rocky planet orbiting a star beyond the Sun.
It might look like a lightsaber floating in space, but the red beam in the middle of this image is actually a galaxy seen edge-on.
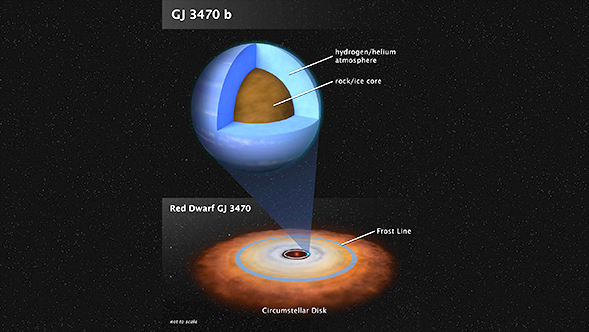
Two NASA space telescopes have teamed up to identify, for the first time, the detailed chemical "fingerprint" of a planet between the sizes of Earth and Neptune. No planets like this can be found in our own solar system, but they are common around other stars.
Unlike Andy Warhol's famous silkscreen grids of repeating images rendered in different colors, the varying hues of this galaxy represent how its appearance changes in different wavelengths of light - from visible light to the infrared light seen by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope.
After nearly 16 years of exploring the cosmos in infrared light, NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope will be switched off permanently on Jan. 30, 2020. By then, the spacecraft will have operated for more than 11 years beyond its prime mission, thanks to the Spitzer engineering team's ability to address unique challenges as the telescope slips farther and farther from Earth.
The evolution of stellar families - born from the same clumps of gas and dust - is just some of what's on display in this sweeping image.
NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope has revealed that some of the universe's earliest galaxies were brighter than expected. The excess light is a byproduct of the galaxies releasing incredibly high amounts of ionizing radiation. The finding offers clues to the cause of the Epoch of Reionization, a major cosmic event that transformed the universe from being mostly opaque to the brilliant starscape seen today.
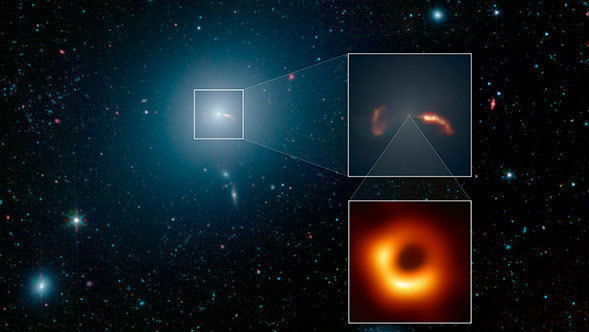
On April 10, 2019, the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) unveiled the first-ever image of a black hole's event horizon, the area beyond which light cannot escape the immense gravity of the black hole. That giant black hole, with a mass of 6.5 billion Suns, is located in the elliptical galaxy Messier 87 (M87). EHT is an international collaboration whose support in the U.S. includes the National Science Foundation.
What looks like a red butterfly in space is in reality a nursery for hundreds of baby stars, revealed in this infrared image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. Officially named Westerhout 40 (W40), the butterfly is a nebula — a giant cloud of gas and dust in space where new stars may form.
Three images from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope show pairs of galaxies on the cusp of cosmic consolidations. Though the galaxies appear separate now, gravity is pulling them together, and soon they will combine to form new, merged galaxies.
Using data from NASA's Kepler space telescope, citizen scientists have discovered a planet roughly twice the size of Earth located within its star's habitable zone, the range of orbital distances where liquid water may exist on the planet's surface. The new world, known as K2-288Bb, could be rocky or could be a gas-rich planet similar to Neptune. Its size is rare among exoplanets - planets beyond our solar system.
Astronomers, astrophysicists and other space scientists will gather to discuss their latest research at the 233rd meeting of the American Astronomical Society this week (Jan. 6-10) in Seattle. Media can watch via the AAS website as research results featuring data from NASA missions are presented at news conferences throughout the week.
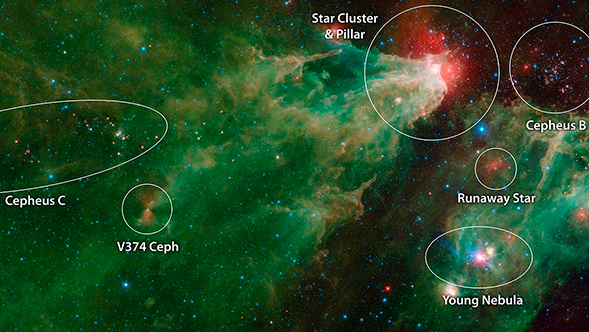
Researchers have discovered a young star in the midst of a rare growth spurt—a dramatic phase of stellar evolution when matter swirling around a star falls onto the star, bulking up its mass. The star belongs to a class of fitful stars known as FU Ori's, named after the original member of the group, FU Orionis (the capital letters represent a naming scheme for variable stars, and Orionis refers to its location in the Orion constellation). Typically, these stars, which are less than a few million years old, are hidden behind thick clouds of dust and hard to observe.
We are all, quite literally, made of star dust. Many of the chemicals that compose our planet and our bodies were formed directly by stars. Now, a new study using observations by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope reports for the first time that silica - one of the most common minerals found on Earth - is formed when massive stars explode.
In November 2017, scientists pointed NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope toward the object known as 'Oumuamua - the first known interstellar object to visit our solar system. The infrared Spitzer was one of many telescopes pointed at 'Oumuamua in the weeks after its discovery that October.
This image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows the Cat's Paw Nebula, so named for the large, round features that create the impression of a feline footprint. The nebula is a star-forming region in the Milky Way galaxy, located in the constellation Scorpius. Estimates of its distance from Earth range from about 4,200 to about 5,500 light-years.
Initially scheduled for a minimum 2.5-year primary mission, NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope has gone far beyond its expected lifetime and is still going strong after 15 years.
Displaying news 31 - 60 of 516 in total