Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/T. Pyle (SSC)
Artwork • January 9th, 2007 • sig07-003b
sig07-003b
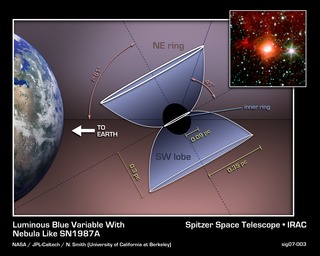
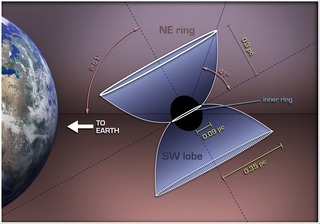
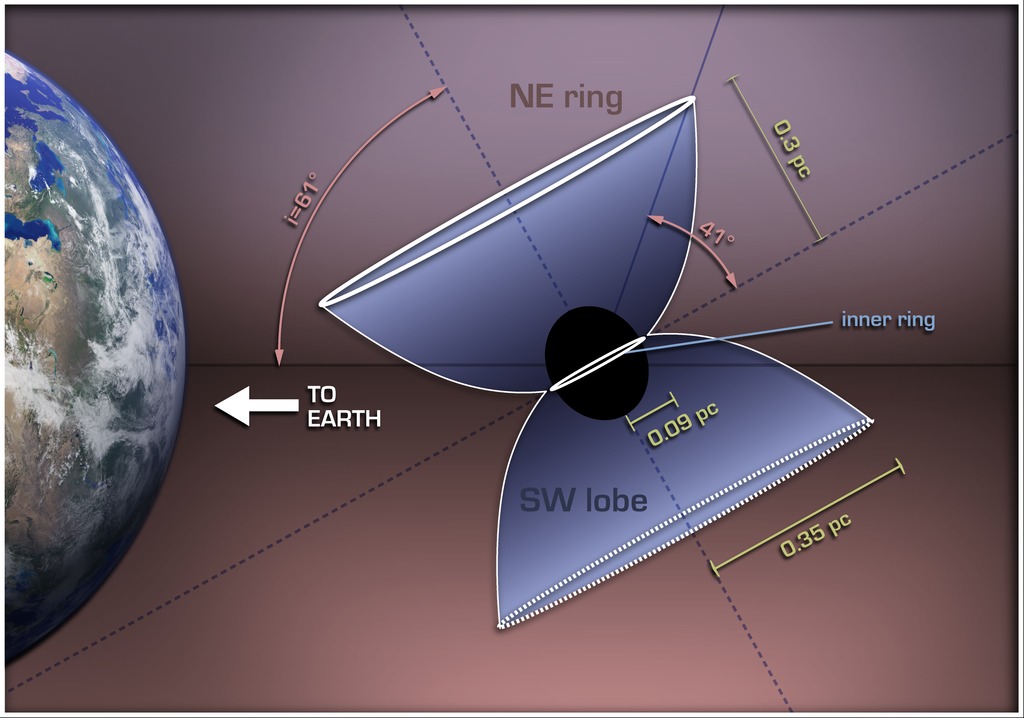
This illustration shows how a Luminous Blue Variable star in our galaxy, named HD168625, is surrounded by a bipolar nebula that is similar to the one around SN1987A. SN1987A was a supernova in the Large Magellanic Cloud that was first seen on Earth in 1987, and was the nearest supernova detected in about 400 years.
The diagram explains the bipolar nebula around HD168625, which has a geometry that makes it a near twin of the famous nebula around SN1987A. Rings near the equator are sometimes seen around stars that shed mass from their surfaces, but the larger rings above the poles are very rare. Tipped toward Earth and illuminated by the star, the rings look like ellipses in images taken with NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope.
The massive star at the center, which lies within the constellation Sagittarius, is about 7,200 light-years from Earth.
About the Object
- Name
- HD 168625
- Type
- Star > Type > Variable
- Nebula
- Star > Evolutionary Stage > Blue Supergiant
- Star > Evolutionary Stage > Supernova
- Star > Circumstellar Material > Outflow
- Nebula > Type > Supernova Remnant
- Distance
- 7,176 Light Years