Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/T. Pyle (SSC)
Artwork • October 27th, 2008 • ssc2008-19a
ssc2008-19a
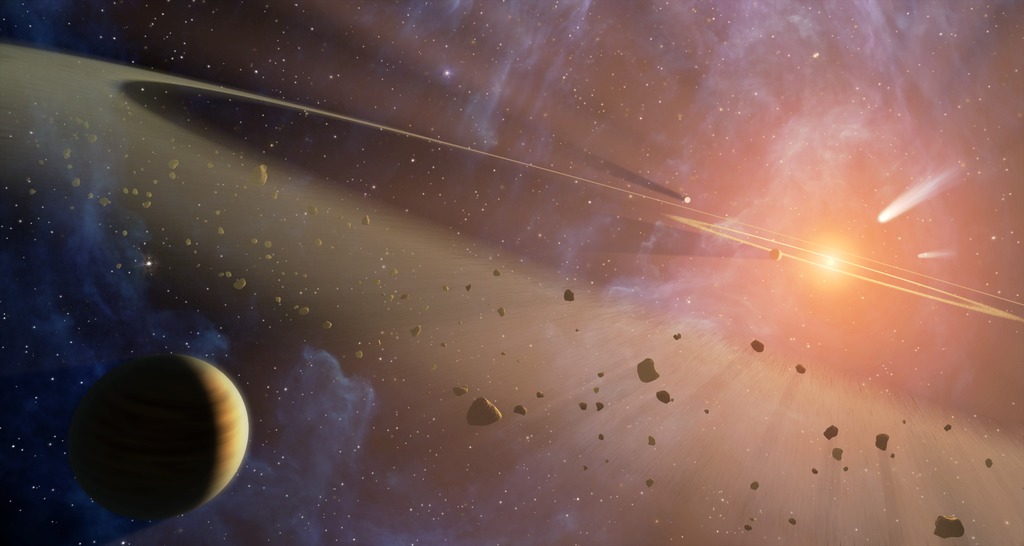
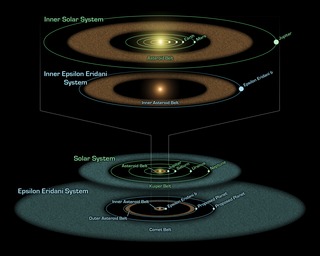
This artist's conception shows the closest known planetary system to our own, called Epsilon Eridani. Observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope show that the system hosts two asteroid belts, in addition to previously identified candidate planets and an outer comet ring.
Epsilon Eridani is located about 10 light-years away in the constellation Eridanus. It is visible in the night skies with the naked eye.
The system's inner asteroid belt appears as the yellowish ring around the star, while the outer asteroid belt is in the foreground. The outermost comet ring is too far out to be seen in this view, but comets originating from it are shown in the upper right corner.
Astronomers think that each of Epsilon Eridani's asteroid belts could have a planet orbiting just outside it, shepherding its rocky debris into a ring in the same way that Jupiter helps keep our asteroid belt confined. The planet near the inner belt was previously identified in 2000 via the radial velocity, or "star wobble," technique, while the planet near the outer belt was inferred when Spitzer discovered the belt.
The inner belt orbits at a distance of about 3 astronomical units from its star -- or about the same position as the asteroid belt in our own solar system (an astronomical unit is the distance between Earth and our sun). The second asteroid belt lies at about 20 astronomical units from the star, or a position comparable to Uranus in our solar system. The outer comet ring orbits from 35 to 90 astronomical units from the star; our solar system's analogous Kuiper Belt extends from about 30 to 50 astronomical units from the sun.
About the Object
- Name
- Epsilon Eridani
- Type
- Star > Circumstellar Material > Disk > Protoplanetary
- Planet > Type > Terrestrial
- Planet > Type > Gas Giant
- Interplanetary Body > Asteroid
- Interplanetary Body > Comet
- Distance
- 10 Light Years