Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/P. Barmby (Harvard-Smithsonian CfA)
Observation • June 6th, 2006 • ssc2006-14a3
ssc2006-14a3
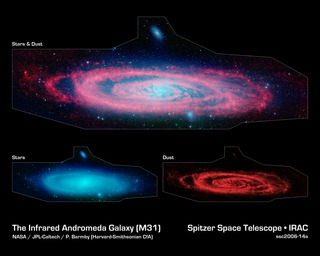
This infrared image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows the Andromeda galaxy, a neighbor to our Milky Way galaxy. The image highlights the galaxy's choppy waves of dust. Spiral galaxies tend to form new stars in their dusty, clumpy arms, while their cores are populated by older stars.
The Spitzer view also shows Andromeda's dust lanes twisting all the way into the center of the galaxy, a region that is crammed full of stars. In visible-light pictures, this central region tends to be dominated by starlight.
A small, companion galaxy called NGC 205 is visible above Andromeda. Another companion galaxy called M32 can also been seen below the galaxy.
The Andromeda galaxy, also known affectionately by astronomers as Messier 31, is located 2.5 million light-years away in the constellation Andromeda. It is the closest major galaxy to the Milky Way, making it the ideal specimen for carefully examining the nature of galaxies. On a clear, dark night, the galaxy can be spotted with the naked eye as a fuzzy blob.
Andromeda's entire disk spans about 260,000 light-years, which means that a light beam would take 260,000 years to travel from one end of the galaxy to the other. By comparison, the Milky Way is about 100,000 light-years across. When viewed from Earth, Andromeda occupies a portion of the sky equivalent to seven full moons.
Because this galaxy is so large, the infrared images had to be stitched together out of about 3,000 separate Spitzer exposures. The light detected by Spitzer's infrared array camera at 8-microns shows warm dust and is shown in red. The contribution from starlight has been subtracted from the 8-micron image to better highlight the dust structures.
About the Object
- Name
- Andromeda Galaxy • Messier 31 • M31 • NGC 224 • Messier 32 • M32 • Messier 110 • M110
- Type
- Galaxy > Type > Spiral
- Distance
- 2,500,000 Light Years
Color Mapping
| Band | Wavelength | Telescope |
| Infrared | 8.0 µm | Spitzer IRAC |
Astrometrics
- Position (J2000)
- RA =0h 41m 53.4s
- Dec = 41° 21' 56.7"
- Field of View
- 3.5 x 1.2 degrees
- Orientation
- North is 50.0° left of vertical